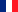
By galvanic anodes
Cathodic protection in harbours is mostly executed by means of galvanic anodes. In most cases zinc or aluminium-indium anodes are used. Depending on the salt degree of the water, sheet piling and jetties may be protected by magnesium anodes also.
Nowadays Al-In-Zn anodes are the most common used anode type. Depending on the metal surface, the applied coating and the life time of the cathodic protection system Anotec’s engineers calculate the most appropriate anode metal, anode weight and dimensions. Harbour anodes may be welded directly to sheet piling or round piles but the use of brackets make it easier to replace the anodes when they are used. It also implicates a far lower installation cost due to a shorter diving time.
For your new project please indicate following characteristics :
- Type of installation : round piles diameter - sheet piling type
- Coating : no coating - number of layers (thickness)
- Surface : square meters immersed and square meters in soil
- Type of water : sea water - brackish - river water
- Use of brackets or welded
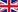
By impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP)
Impressed current systems have some advantages towards galvanic anode systems in harbour structures :
- Low total cost of ownership
- Communication of cathodic protection data
- Less diving costs (less anodes)
- May be used with uncoated structures due to a higher driving force
- Use in ATEX areas is allowed using polarisation cells.
It’s always worthwhile to engineer both methods for your project.
Please contact our sales and engineering staff and they will be help you to define the most appropriate system.